Problem Statement
Nigeria’s innovation ecosystem drives entrepreneurship, supports startups, and fosters economic growth. However, these hubs face significant challenges, including limited access to funding, inadequate infrastructure, and gaps in capacity-building initiatives. Addressing these issues is critical for maximising their impact and positioning Nigeria as a leader in innovation across Africa.
Data Collection & Analysis
DigitA’s approach to data collection was deployed through comprehensive surveys and interviews with stakeholders across Nigeria’s innovation landscape. The in-depth assessment focused on over 190 Hubs within Nigeria’s Innovation Support Network (ISN). Hubs were made to provide details about their operations, including their legal structures, sectoral focus, revenue models, and challenges. Quantitative data was complemented with qualitative insights to ensure a balanced understanding of the ecosystem.
Key Insights Include:
- Geographic Distribution: Hubs are spread across Nigeria, with Lagos and Abuja hosting the largest concentrations. Other hubs operate in both urban and rural settings, highlighting their diverse reach.
Fig 1– Geographic Distribution of Hubs by Location
- Staffing and Operations: Most hubs employ fewer than ten full-time staff, reflecting their small to medium size. Staff roles are concentrated in administration, mentorship, marketing, and technical support.
- Sectoral Focus: Key sectors include ICT (38.3%), Agritech (15.9%), Fintech (11.2%), and Edutech (15%), while sectors like health tech (4.7%) and cleantech (1.9%) are underrepresented, highlighting the need for diversification in healthcare and sustainability.
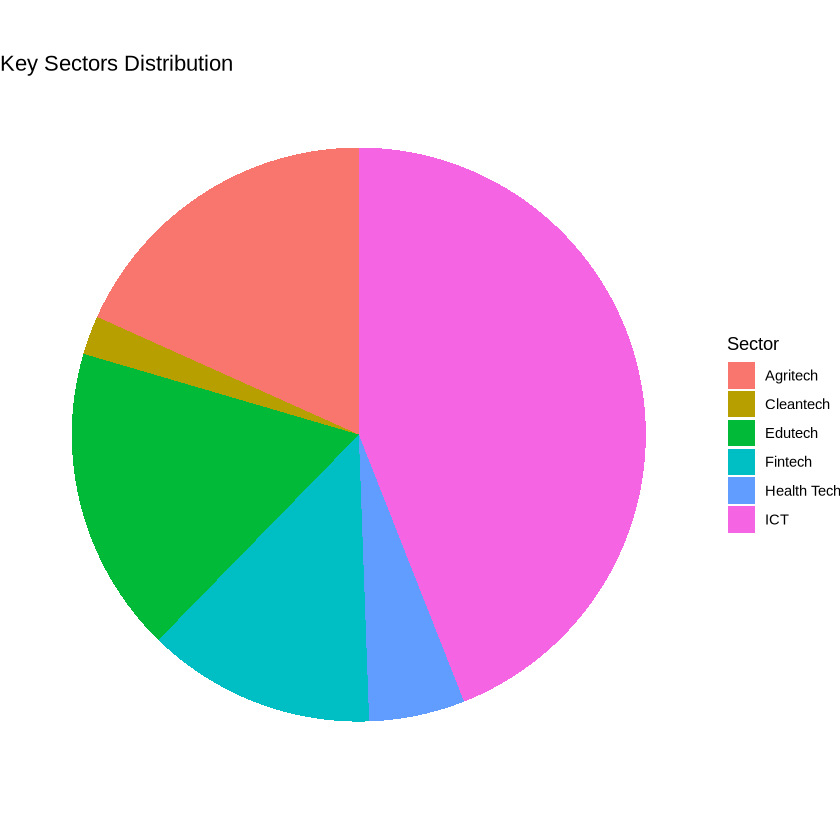
Fig 2 – Key Stakeholder Percentage
- Revenue Streams: Primary revenue sources include membership fees, consulting services, and external grants. However, over 70% of hubs report annual revenues below $50,000, underlining the financial constraints they face.
- High Operational Costs: Hubs face significant financial pressures from wages, rent, and energy expenses, especially in areas with unreliable electricity. Over 60% report frequent power outages, forcing investment in alternative energy solutions. Poor internet connectivity further hinders productivity and innovation.
- Lack of Policy Support: The absence of a comprehensive innovation policy leaves hubs without the coordinated funding, training, and collaboration needed for growth. This limits their ability to scale and effectively support startups.
- Limited Resources: Many hubs struggle with insufficient funding, which affects their ability to offer startup tools, mentorship, and infrastructure. Poor road networks exacerbate their isolation, reducing collaboration opportunities.
- Skill Gap: Attracting and retaining skilled talent remains challenging, with 75% of hubs citing a growing skills gap. Even when talent is available, 45% struggle to convert theoretical knowledge into practical solutions, stalling innovation.
- Lack of Collaboration: Collaboration is critical, but 40% of hubs operate in silos, missing opportunities for shared resources, knowledge, and networks.
This robust data collection and analysis process ensured that solution development recommendations were grounded in evidence, making them actionable and relevant to the needs of Nigeria’s innovation hubs.
DigitA’s Approach to Solution Development
To address the challenges identified, DigitA recommended targeted interventions informed by the collected data:
- Enhancing Funding Opportunities: – Introduce hybrid funding models that combine grants with revenue from consulting services, event hosting, and co-working spaces. – Establish partnerships with venture capital firms and corporate sponsors to provide consistent financial support.
- Infrastructure Development: – Advocate for improved access to reliable electricity and internet connectivity, particularly in underserved regions. Promote the adoption of renewable energy solutions, such as solar power, to reduce reliance on unstable energy sources.
- Capacity Building: – Develop training programs for hub managers and staff, focusing on financial planning, sustainability practices, and digital skills. Facilitate knowledge-sharing networks among hubs to foster collaboration and the exchange of best practices.
- Sectoral Specialisation: – Encourage hubs to identify and build expertise in specific sectors, such as Agritech or Fintech, to enhance their competitive edge. – Support hubs in accessing international markets through cross-border collaborations and strategic alliances.
- Strengthening Public-Private Collaboration
Mentorship programs, tax benefits for CSR initiatives, and innovation summits can foster knowledge sharing, ecosystem integration, and funding access. - Expanding Service Offerings
Hubs should diversify into areas like financial literacy, mental health, and sectoral growth in health tech and cleantech to attract investment and support community needs. - Ensuring Financial Sustainability
Adopting revenue models like coworking rentals and event hosting, alongside grant-writing workshops, can improve financial independence. - Promoting Ecosystem Collaboration
Peer mentorship, regional clusters, and digital platforms can foster resource sharing and collective innovation. - Accelerating Growth and Measuring Success
Strategic partnerships and tracking metrics like energy adoption, internet access, and sectoral diversification will ensure sustainable hub growth.
These solutions aim to strengthen the operational capacity and sustainability of innovation hubs, ensuring they can effectively serve their communities.
Implementation & Monitoring
DigitA also recommended a phased approach to implementation to be complemented with an ongoing monitoring process to measure progress. This process should include;
- Implementation:
- Partnering with government agencies and private sector players to fund infrastructure projects.
- Rolling out targeted training programs for hub staff and management, delivered both online and in person.
- Developing a centralised platform to facilitate collaboration and resource sharing among hubs.
- Monitoring:
- Tracking key performance indicators, including revenue growth, job creation, and the number of startups supported.
- Conducting annual surveys to assess the satisfaction of hub members and identify emerging challenges.
- Regularly evaluating the effectiveness of partnerships and funding initiatives, adjusting strategies as needed.
Conclusion
DigitA’s findings in the assessment of the hubs underscore the importance of data-driven decision-making in achieving successful digital transformation. Nigeria’s innovation hubs can maximise impact and solidify their position as key drivers of economic growth and technological advancement if financial, infrastructural, and capacity-building challenges are addressed. Collaborative efforts from government, private sector players, and international partners will be essential in realising this vision. Building a resilient and inclusive ecosystem that empowers innovators, supports startups, and contributes to sustainable development across the nation can truly support entrepreneurship and foster economic growth.
